Tesla vs. permanent magnets: the battle for the future of electric vehicle power technology
Tesla vs. permanent magnets: the battle for the future of electric vehicle power technology
1.1 History and Importance of Electric Vehicles
In the age of traditional fuel cars, the engine was hailed as the heart of the car because it performed the important task of energy conversion. However, with the rise of electric vehicles, our focus has gradually shifted to battery storage, often ignoring the importance of motors. In fact, electric motors are widely used in all corners of our lives, but the strict requirements for power, torque, heat dissipation, noise, and output pulse required for drive motors remain a technical challenge. Next, we will explore together the basics of power motors and uncover the technical mysteries behind them.
Electric motor relays for electric vehicles are developing rapidly, and their critical properties are widely used in all areas of life, but the field of drive motors still faces technical and challenges.

1.2 Permanent magnet motors and induction motors
Motor, as the key equipment of energy conversion, plays a vital role in the field of new energy resources vehicles. It not only has the dual function of an electric motor and a generator, but also can be selected according to different energy supply types, such as electric motors such as DC, AC, permanent magnetic brushless or switch magnetic resistance. In the drive system of new energy resources vehicles, permanent magnet synchronous motor, AC asynchronous motor and switched reluctance motor are the three main choices. Their structural characteristics and control methods vary, so the range of applications in the automotive market also varies.
Permanent magnetic motors and induction motors are two schools of wide application, with Tesla being the representative of induction motor, while permanent magnetic motor is used by many manufacturers.
2.1 Permanent magnetic synchronous motors and asynchronous motors
In the field of passenger cars, motor technology is mainly divided into two schools of technology: induction motor and permanent magnet motor. Tesla is the representative of induction motors (asynchronous motors), while permanent magnets are more widely used, such as BMW and many domestic electric vehicle manufacturers. What are the differences between these two motors?
A permanent magnet motor, also known as a synchronous motor, uses a permanent magnet for its rotors, and the electromagnetic torque generated by the stator pushes the rotor magnetic field around the axis, achieving synchronization between the statore and the rotor's magnetic field. Induction motor, namely asynchronous motor, is through the stator winding rotating magnetic field and rotor winding induced current magnetic field interaction, produce electromagnetic torque drive rotor rotation.
There are obvious differences between permanent magnet and asynchronous motors in structure and control, affecting their different applications in the automotive market.
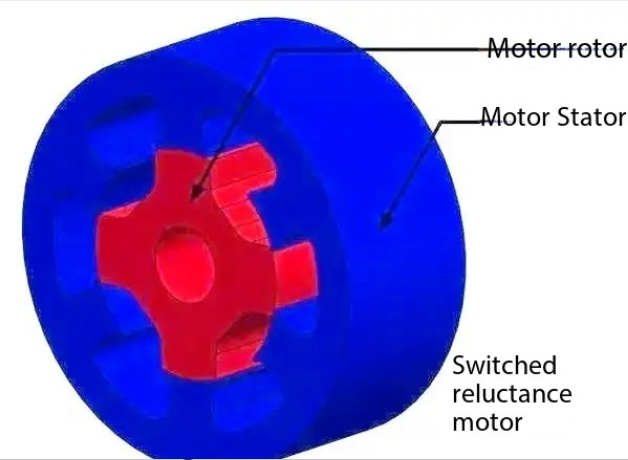
2.2 ◇ Switching magnetic resistor motor characteristics
In addition, in the field of commercial vehicles, switching magnetic resistor motors have also been widely used and shown good development prospects. Its advantage is that it does not need to use magnetically hard material, does not depend on rare earth, and omits common copper coil in the motor, so the cost is relatively low. Switching magnetic resistor motors have two basic characteristics: one is switchability, the motor needs to work in a continuous switching mode; The second is the reluctance, the stator and rotor with variable reluctance magnetic circuit, more specifically, it is a doubly salient pole generator.
Switched magnetic resistor motors have speed flexibility and high efficiency, but require improvements in vibration and noise control.
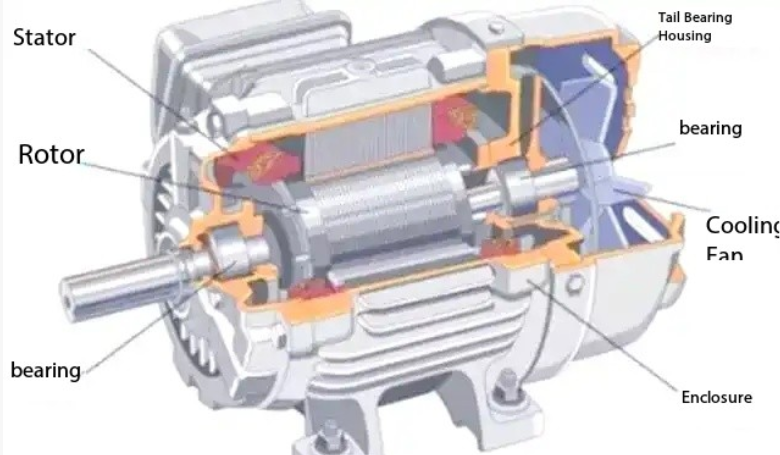
3.1 Properties of AC asynchronous motors
Diagram of AC asynchronous motor structure
The power system of electric vehicles is very different from that of internal combustion vehicles, and its core components include the energy storage mechanism (ESS) that stores energy, which transfers energy to the converter and the power control module (PEM). Sensors sense the driver's operating intentions and road conditions, and in turn drive the executive motor (motor) to work.
AC asynchronous motors have a long history and are the power foundation of Tesla cars. Its structure consists of key parts such as stator and rotor.
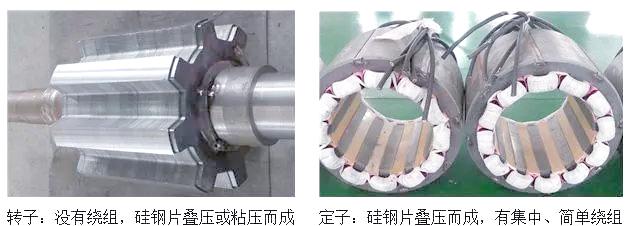
3.2 ◇ Tesla's Innovative Design
The power electronic module of Tesla vehicles efficiently converts direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power for use in induction motors by employing 72 Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs). This module not only controls the charging and discharging rates of the vehicle but also precisely regulates voltage levels, motor speed (RPM), torque, and the regenerative braking system. The regenerative braking system is a critical technology in Tesla vehicles, as it captures and recovers the kinetic energy generated during braking, thereby further optimizing energy efficiency.
Tesla's induction motor design is compact, enhancing the performance of electric vehicles through lightweight construction and optimized heat dissipation.
3.3 Lightweighting and Efficiency Challenges
The induction (asynchronous) motor used by Tesla is, specifically, a 3 phase 4 pole induction motor. The rotational speed n of this motor can be calculated by formula (1-S) 60f / P, where S is the slip, f is the power frequency, and P is the polar log. By controlling the current frequency of the stator coil, we can change the rotation strength of the electromagnetic field and in turn control the speed of the motor. Under the effect of induction magnetic field, the induction electromotive force is generated by cutting the magnetic induction wire, and the induction current is generated in the rotor winding. These induction currents interact with the magnetic field to produce an electromagnetic torque that drives the rotor to rotate. In simple terms, it is by adjusting the frequency of alternating current to change the speed of the electric motor, thereby driving the car forward.
Although Tesla electric motors are lightweight and efficiently controlled, they still need to address energy consumption and cost challenges.
